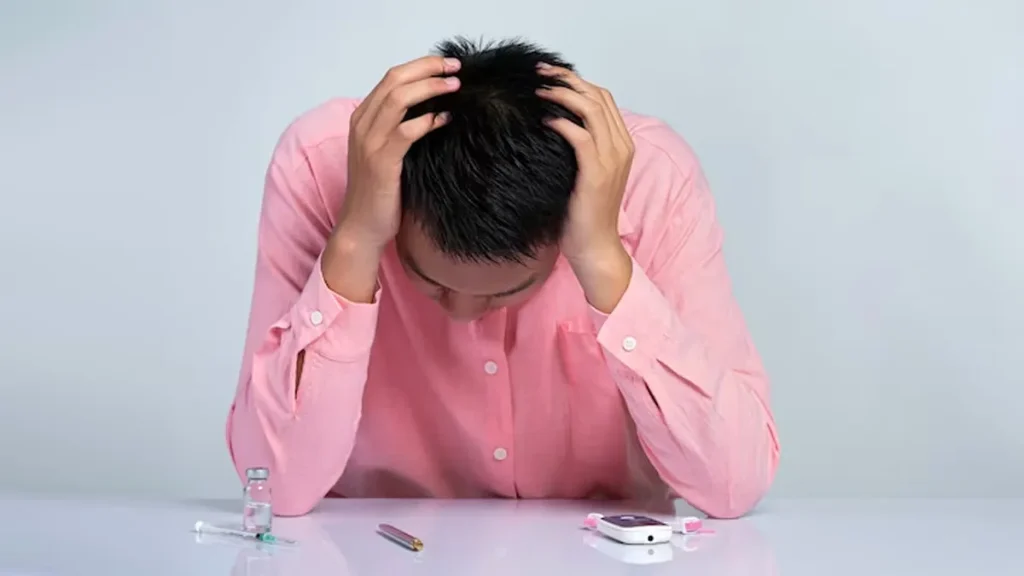
A recent study has found a strong connection between loneliness, social isolation, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Researchers emphasize that emotional well-being is just as important as diet and exercise when it comes to preventing chronic health conditions.
According to the findings, individuals who often feel lonely or lack regular social interaction are at significantly higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes over time. The emotional stress caused by prolonged isolation may trigger hormonal imbalances and lifestyle changes that contribute to insulin resistance.
The research also highlights that middle-aged and older adults are particularly vulnerable, especially those living alone or without consistent social support. Experts urge communities and healthcare systems to prioritize mental and emotional health as part of routine diabetes prevention strategies.
The study did not find a similar link with general depression, indicating that loneliness and isolation have a unique and independent impact on physical health. Addressing these emotional factors could potentially reduce the global burden of diabetes, especially as populations continue to age.
Healthcare professionals recommend staying socially active, participating in group activities, and seeking emotional support to lower diabetes risk and improve overall well-being. This study serves as a wake-up call for societies to view emotional health as a key pillar of chronic disease prevention.


Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment