Indonesia’s collaboration with the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has come to an uncertain halt, leaving critical health programs in limbo. The Southeast Asian nation, which has received substantial support from USAID for various public health initiatives, is now grappling with the potential long-term consequences of this pause.
As part of the larger restructuring plan under the previous U.S. administration, the USAID might be merged into the State Department, reshaping how foreign aid is distributed. The ramifications of this change are far-reaching, particularly for Indonesia’s ongoing battle against tuberculosis (TB) and HIV, which have become major public health concerns.
The Impact on Indonesia’s Healthcare System
Since 2020, USAID has invested over $800 million into Indonesia’s health sector. This support has been instrumental in combating diseases like tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS. However, as the U.S. evaluates its foreign aid strategy, Indonesia faces a critical challenge.
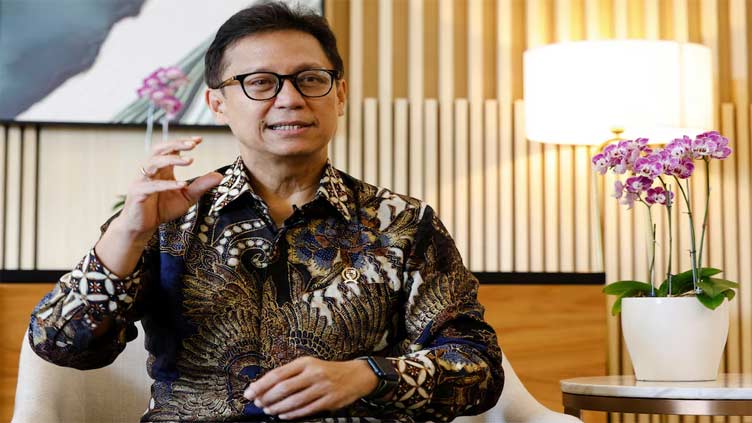
Health Minister Budi Gunadi Sadikin stated that the projects with USAID are currently “on hold” but emphasized that no decision has been made regarding their permanent suspension. He noted that further clarity is expected in the next few months, leaving the health sector in a state of uncertainty.
The impact of this pause is already being felt, particularly as Indonesia has seen a significant rise in TB cases, with over 1 million reported in 2023. These developments threaten to reverse progress made in fighting infectious diseases, as resources from USAID were key in funding medical treatments and preventive measures.
Other Key Support Systems at Risk
Beyond direct funding from USAID, Indonesia also receives support from other global health organizations like the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria. However, without sufficient financial backing from USAID, Indonesia’s efforts to tackle these diseases may face serious setbacks.
Experts, including Olivia Herlinda from the Center for Indonesia’s Strategic Development Initiatives, have warned that this pause could lead to widespread health challenges. USAID has supported Indonesia in a variety of health sectors, including maternal and child health, pandemic preparedness, and disease prevention. The potential loss of this support could hinder the country’s ability to meet its public health goals.
Indonesia’s Plan to Combat Health Challenges
Despite the uncertainty surrounding USAID support, Indonesia is moving forward with its own initiatives to address public health issues. Starting in February 2025, the government will launch an extensive nationwide health screening program, aiming to reach 220 million people within the year. This program, with a budget of approximately $184 million, will focus on preventing early deaths from major diseases such as stroke, heart disease, and tuberculosis.
As one of the world’s most populous nations, Indonesia’s success in tackling these health challenges will be crucial not only for its own citizens but for the global community’s efforts to combat infectious diseases.
Conclusion
The future of health programs in Indonesia remains uncertain as USAID re-evaluates its priorities. While the pause on health partnerships raises concerns, Indonesia is committed to strengthening its healthcare system and continuing its fight against the rising rates of tuberculosis, HIV, and other critical health threats


Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment